Introduction of UDP
There are
two transport layer protocols: TCP and UDP. TCP – Transmission control
Protocol and UDP – User Datagram Protocol. In this post, we will discuss
about UDP.
UDP
stands for User Datagram Protocol. UDP is a simple, datagram-oriented transport
layer protocol. UDP has been designed to transfer data packet over internet.
UDP is connectionless protocol provides no reliability or flow control
mechanisms. It also has no error recovery procedures. Several application layer’s
protocols such as TFTP and the RPC use UDP. UDP makes use of the port concept
to direct datagrams to the proper upper-layer applications. UDP serves as a simple application interface
to the IP.
Requirement
of UDP:
TCP
proves to be an overhead for certain kinds of applications. The Connection
Establishment Phase, Connection Termination Phase etc of TCP are
time consuming. To avoid this overhead, certain applications which require fast
speed and less overhead use UDP. UDP is used, where acknowledgement uses
significant bandwidth along with original data packet.
UDP Header
 |
| Figure: Encapsulation of UDP Datagram |
Above figure
shows the encapsulation of a UDP datagram as an IP datagram.
 |
| Figure: UDP Datagram |
Above figure shows the format of the UDP header. The port number identify the sending
process and the receiving process.
Source
Port: Source port number identifies the port of the sending
application process.
Destination
Port: Destination port number identifies the receiving process on
the destination host machine.
UDP
Length: The UDP length field is the length of the UDP data in bytes.
The minimum value for this field is 8 bytes.
UDP
Checksum: UDP checksum covers the UDP header and the UDP data. Both UDP
and TCP include a pseudo-header with the UDP datagram just for the checksum
calculations.
Data: Data
field size is variable. It contains user data.
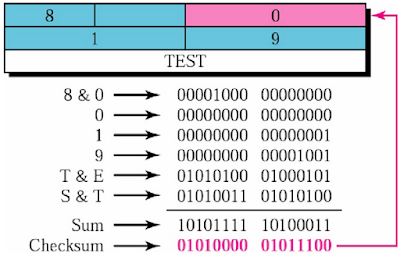
UDP Checksum Example
UDP checksum calculate from UDP header and UDP datagram part. Purpose of UDP header is check error in datagram. First of all, at sender side checksum has been calculated and checksum value added in checksum field. Again, checksum is calculated at receiver end, if there is mismatch in both the value, then datagram must be discarded by receiver, because no error recovery in UDP datagram. But in some of the application packet is pass to that application with warning. Here, below there is one example of UDP checksum.
Realtime application of UDP
Broadcasting
and multicasting applications use UDP protocols.
Streaming
media applications such as movies.
Online chatting
and online multiplayer games.
Voice
over IP (VoIP).
UDP is used
with the RTOS (real time operating systems).
UDP is
used in aircraft controls and flight instruments.
DNS uses
UDP protocol, because immediate response is required in DNS.
Network
layer protocols like RIP and UDP uses UDP because, it transfers very less
amount of data.
Other
protocols associated with UDP are Kerberos, Network Terminal Protocol (NTP), Network News Protocol
(NNP) etc…
To learn more about UDP Header, Click here
Watch more videos click here.
No comments:
Post a Comment