Introduction of IP
IP stands
for Internet Protocol. IP is network layer protocol. There are two types of IP
format – IP Version 4 (IPV4) and IP Version 6 (IPV6).
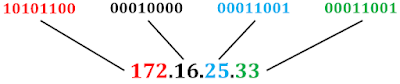
IP address is also called logical address. IP is connection less protocol. Packets in the IPv4 layer are called datagrams. A datagram consisting of two parts: Header and data. IP address is assigned to end devices and intermediate devices like computers, routers, manageable switches. IP address is written in two types of notations: IPV4 written in dotted decimal notation and IPV6 written in hexadecimal notation. In this post, we are discussion about IPV4 header. Example of IPV4 dotted decimal notation is below:
Need of
IP address
IP address is used for host-to-host communication between two or more devices in same network or different network. Source sends data to destination using IP address, IP address is an address having information about how reach specific destination.
IPV4 Header
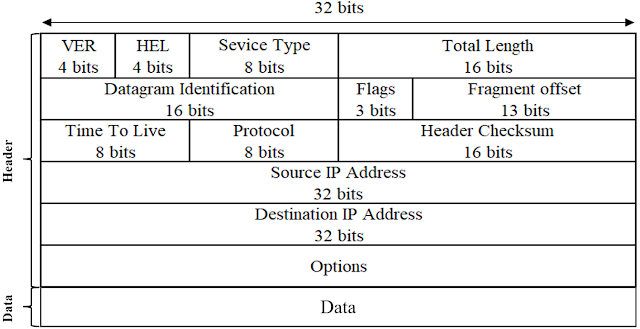 |
| Figure: IPV4 Header Structure |
Above
figure shows the format of the IPV4 header.
VER: This field contains the version of IP.
HLEN: It is the length of the IP header. It is 32 bits.
Service Type: This service type is an indication of the quality
of service requested for this IP datagram. Ex., Less Delay, High Throughput,
Reliability of packet.
Total Length: It specifies the total length of the datagram.
Datagram
= Header + Data.
Header =
20 Bytes to 60 Bytes
Data = 20
Bytes to 65535 Bytes
Datagram Identification: It is a unique number assigned by
the sender used with fragmentation.
Flags: it contains 3 bits:
a. The 1st
bit is reserved and must be zero.
b. The 2nd
bit is DF (Do not fragment), 0 means allow fragmentation.
c. The 3rd
bit is MF (More fragment), 0 means least fragment.
Fragment Offset: It is used to reassemble the full datagram.
TTL: TTL stands for Time to live. It is specifying the time;
datagram is allowed to travel.
Protocol Number: It indicates the higher layer protocol to
which IP should deliver the data in this datagram. E.g., ICMP = 1, TCP = 6, UDP
= 17.
Header Checksum: It is a checksum for the information
contained in the header. If the header checksum does not match the contents,
the datagram is discarded.
Source IP address: It specify the logical address of sender.
Destination IP address: It specify the logical address of
destination.
IP Options: It is a variable length field used for control or
debugging and measurement. E.g., Timestamp, security and record route etc…
Realtime application of IP address
Access Website on internet: Without IP address we cannot
access internet. If you are access any website on internet, IP address is
required. Because all the webservers on internet is configure using IP address
Domain Name System (DNS): DNS is one kind of distributed
database. Using the DNS, managing host names and their associated IP addresses.
IP filtering: IP filtering using firewall and protect their network
from attackers.
Telnet: Telnet is a protocol that enables you to log onto
and use a remote computer as though you were connected directly to it. Without
IP address, you cannot access remote computer.
To learn more about IPV4 Header, Click here
Watch more videos click here.
No comments:
Post a Comment